Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
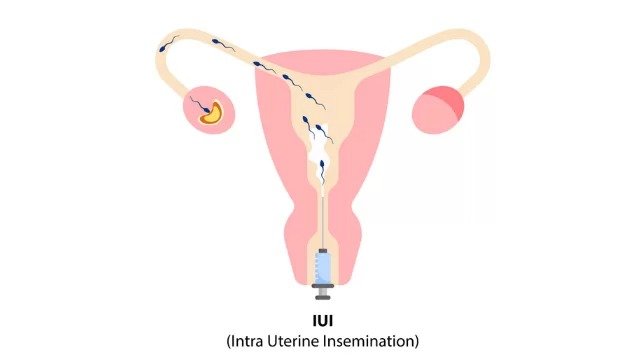
Introduction:
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment that assists couples in their journey to parenthood. It’s a less invasive option compared to in vitro fertilization (IVF) and can be an effective solution for certain fertility challenges. In this blog, we’ll explore IUI in detail, covering its conditions, types, and treatment process.
Types of IUI:
There are two primary types of IUI:
- Natural Cycle IUI: This method involves tracking the woman’s natural cycle and timing the insemination to coincide with ovulation. It’s suitable for women with regular cycles and healthy ovulation.
- Medicated Cycle IUI: In this approach, ovulation is stimulated through medications such as Clomiphene or gonadotropins. This type is preferred when the woman has irregular cycles or ovulatory issues.
Conditions for IUI:
IUI is recommended for couples who experience specific fertility issues. These include:
- Unexplained Infertility: When there’s no apparent cause for a couple’s infertility.
- Male Factor Infertility: If the male partner has mild sperm abnormalities, IUI can help deliver sperm directly into the uterus.
- Cervical Factor Infertility: When the cervix produces hostile mucus that hinders sperm from reaching the egg.
- Ovulatory Disorders: IUI can be used in conjunction with ovulation-inducing medications to enhance the chances of conception.
- Endometriosis: For couples where the female partner has endometriosis, IUI can help bypass obstacles created by this condition.
The IUI Treatment Process:
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the IUI treatment process:
- Ovulation Monitoring: The woman’s cycle is monitored through ultrasounds and hormone level tests to determine the ideal time for insemination.
- Semen Collection: On the day of insemination, the male partner provides a sperm sample, which is then processed in the laboratory to extract the healthiest sperm.
- Insemination: The processed sperm is placed directly into the woman’s uterus using a thin catheter. This is a quick and painless procedure.
- Post-Insemination Care: After the procedure, the woman may be advised to rest for a short period before resuming normal activities.
- Pregnancy Test: Approximately two weeks after the IUI, a pregnancy test is conducted to determine if the procedure was successful.
Success Rates and Considerations:
The success rates of IUI vary depending on factors such as age, the cause of infertility, and the type of IUI. On average, success rates range from 10% to 20% per cycle. Multiple cycles may be needed for conception.
IUI is a lower-cost, minimally invasive option for couples seeking fertility assistance. However, it may not be suitable for everyone. Couples with severe male factor infertility or damaged fallopian tubes may require more advanced treatments like IVF.
Conclusion:
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) offers hope to couples facing certain fertility challenges. By understanding the conditions, it can address, the types available, and the treatment process, couples can make informed decisions on their journey to parenthood. It’s essential to consult with a fertility specialist to determine if IUI is the right choice for your unique situation.

