Ovarian Cancer
Introduction:
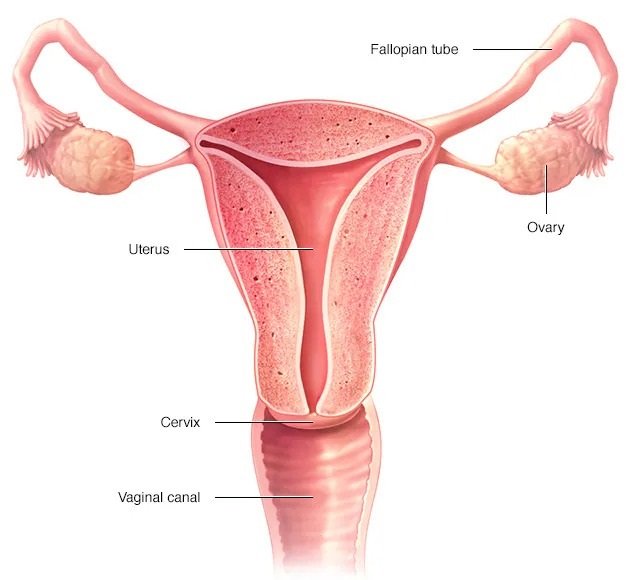
What Is Ovarian Cancer?
The ovaries are the sexual parts of women. They make eggs that can be fertilized. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone are released by them. The second most common type of cancer in women in the US is ovarian cancer. About 1 in 72 women will have this risk at some point in their lives. In general, people are diagnosed at age 63. Over 80% of people who are identified with ovarian cancer are over the age of 40. As you get older, your chance of getting ovarian cancer goes up.
Causes, risks, and ways to lower those risks
Genetic and reproductive factors are often risk factors.
Some reproductive factors can cause periods to start early or menopause to start later than expected. Women who have been pregnant more than once are less likely to get it. Some ways to lower your risk of getting ovarian cancer are to use oral contraceptives, have a tubal closure (tubectomy), or nurse.
A person’s family background or genes are very important in determining their risk of getting ovarian cancer. If a woman has a first-degree cousin with the disease, her chance is about twice as high. The genetic changes that cause ovarian cancer are known as BRCA1 and BRCA2. However, only 10% of cases of ovarian cancer have DNA changes that have been proven to be in BRCA1 or BRCA2. If you have a confirmed inherited BRCA1 gene mutation, your lifetime risk of getting ovarian cancer goes up by 15–45%. If you have a confirmed inherited BRCA2 gene mutation, your risk of getting ovarian cancer goes up by 10–20%.
What ovarian cancer symptoms and signs are
People with ovarian cancer can have either advanced stage acute symptoms (symptoms that come on quickly) or early stage sub-acute symptoms. It’s hard to see the signs, and the growth may grow over time. Because the early signs of ovarian cancer are often very mild and hard to spot, it is one of the most dangerous diseases in women.
There are many vague and general signs that can show up in women with ovarian cancer. Some of these signs are feeling bloated, having a full stomach, abdominal pain, and soreness. Constipation, vaginal bleeding, indigestion, acid reflux, trouble breathing, tiredness, loss of hunger, and weight loss are some of the other signs. Some people may feel lumps or growth in their abdomens when they get a tumor.
Other signs of ovarian cancer are bleeding after menopause, bleeding in the rectal area, and symptoms not related to the cancer itself, like dermatomyositis, anemia, or nephrotic syndrome.
Read more about symptoms and signs.
Finding the cause
A full clinical evaluation should be done on anyone who is thought to have ovarian cancer. The first imaging test that should be done is an ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis. A CT scan can also help people with ovarian cancer figure out how bad their disease is and make better plans for surgery. An X-ray of the chest can help find pleural fluid. Most of the time, an MRI scan is not suggested. The tumor marker CA-125 is usually checked for in people who are thought to have cancer. Also, an upper and lower body endoscopy should be done on people who have complaints related to their intestines.

