Transfemoral Prosthesis
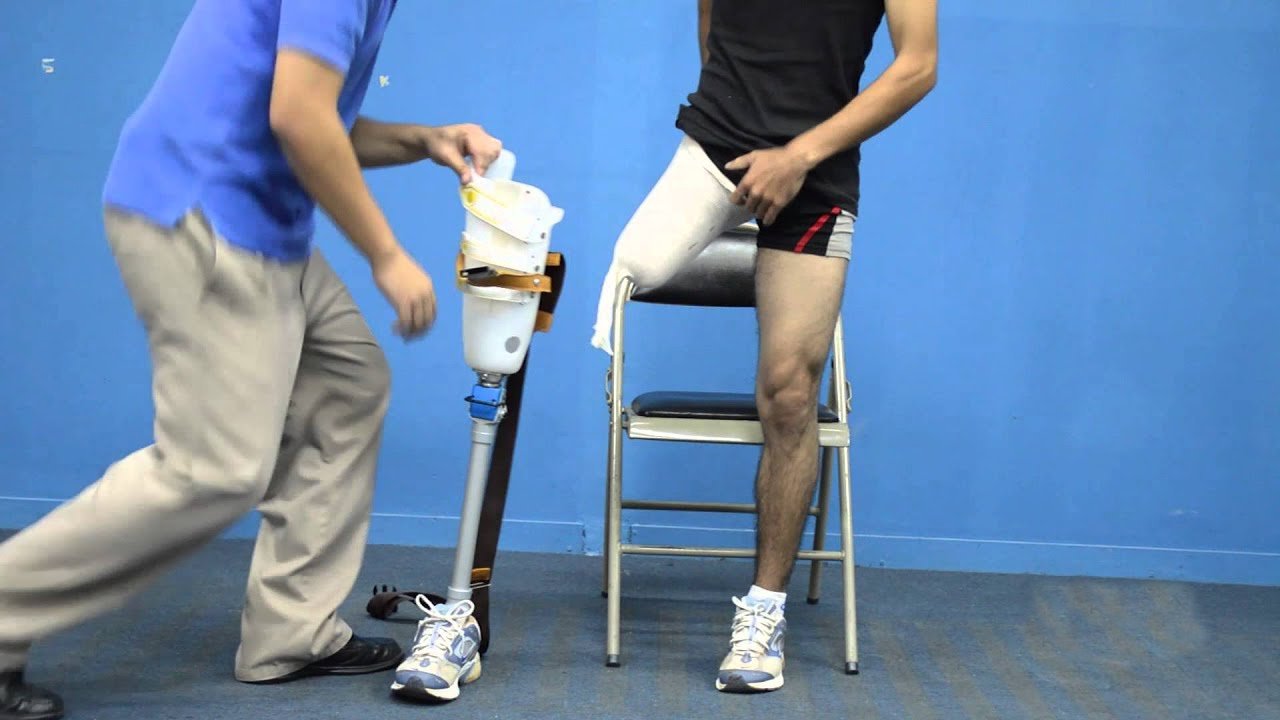
Introduction:
A transfemoral prosthesis is a remarkable technological advancement in the field of prosthetic limbs, designed to help individuals who have lost their leg(s) above the knee regain mobility and independence. This type of prosthesis is essential for amputees who need to restore their lower limb function. In this blog post, we will delve into the conditions that may necessitate a transfemoral prosthesis, the types available, and the treatment options associated with it.
Types of Transfemoral Prosthetic:
- Socket Design: Transfemoral prosthetic sockets come in various designs, including ischial containment sockets (ICS) and quadrilateral sockets. These sockets are custom-made to ensure a snug fit, comfort, and stability for the amputee.
- Knee Joints: There are two primary types of knee joints for transfemoral prostheses: mechanical and microprocessor-controlled. Mechanical knees offer a cost-effective option, while microprocessor-controlled knees use sensors and advanced technology to adjust to walking speeds and terrains.
- Prosthetic Feet: Transfemoral prosthetic feet come in various designs, from rigid to dynamic response feet, each offering different levels of mobility and stability.
Conditions Requiring Debridement:
- Traumatic Amputations: Accidents, such as car crashes or workplace mishaps, can lead to traumatic amputations of the leg above the knee. Transfemoral prostheses offer these individuals a chance to regain their mobility.
- Disease-Related Amputations: Certain medical conditions, such as peripheral arterial disease, cancer, or severe infections, can necessitate amputations above the knee. In such cases, transfemoral prostheses are crucial for maintaining an active lifestyle.
Treatment Options and Rehabilitation:
- Assessment and Consultation: The journey towards a transfemoral prosthesis begins with a comprehensive assessment by a prosthetist. They work closely with the patient to determine their specific needs and goals.
- Customization:The prosthetist customizes the prosthetic socket, knee joint, and foot based on the individual’s residual limb and functional requirements.
- Fitting and Alignment: The prosthetic limb is carefully fitted and aligned to ensure proper function and comfort. This process may require several adjustments to achieve the best results.
- Rehabilitation: After receiving the prosthesis, the amputee undergoes rehabilitation to learn how to use their new limb effectively. This involves gait training, balance exercises, and strengthening routines.
- Ongoing Care: Regular follow-up appointments with the prosthetist are essential to address any issues, make adjustments, and ensure the prosthesis continues to meet the user’s needs.
Conclusion:
Transfemoral prostheses play a pivotal role in improving the quality of life for individuals who have undergone above-knee amputations. These advanced devices are tailored to the unique needs of each user, offering a wide range of customization options. With proper assessment, fitting, and rehabilitation, individuals with transfemoral prostheses can regain their mobility, independence, and confidence, enabling them to lead fulfilling lives. If you or a loved one faces the prospect of using a transfemoral prosthesis, consult with a prosthetist to explore the possibilities of restoring mobility and reclaiming an active lifestyle.
Contact Us
Get In Touch
Address
F 146/9 second floor shaheen bagh jamia Nagar New Delhi 110025
Phone
+91-9716952857
cure2world@gmail.com

